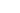What is a CO2 Heat Pump?

Apr 29 2024
Traditional Heat Pumps use refrigerant to change stages based on pressure, transferring heat from inside a building and out (and vice versa in the winter). One of the big costs to heat pumps is Freon, which is expensive, as well as the copper lines running through a building to transfer the heat around via Freon.
There is a new technology breaking that uses CO2 to act as the refrigerant. It is exciting, and we will discuss some reasons it may or may not break out into the US anytime soon.
A Very High Efficiency HVAC system has an air sourced heat pump with an ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilator) and is the cornerstone of our offerings to commercial and public buildings in Illinois. CO2 based heat pumps have the potential to drive the costs down even further on this exciting approach.
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
A heat pump is different than electric heat and operates on a very clever principle that allows it to move heat, rather than generate it directly. This makes it a much more efficient way to heat and cool your commercial building compared to traditional systems like furnaces, boilers and air conditioners. But how exactly does it achieve this?
The key component in a heat pump is refrigerant, a specially chosen liquid that can easily absorb and release heat. The refrigerant circulates through a closed loop system within the heat pump. By changing the pressure of the refrigerant, the heat pump can manipulate its ability to absorb and release heat.

Here’s where the magic happens. In heating mode, the heat pump absorbs heat from the outside air, even when it’s cold outside. Even though the air might feel chilly to us, it still contains some thermal energy. The refrigerant, in its low-pressure state, is able to efficiently capture this heat. Then, the refrigerant is compressed, which significantly increases its temperature.
Finally, the hot refrigerant transfers its heat to the interior of your building, warming you up. The cooled refrigerant then circulates back outside to pick up more heat, and the cycle continues. This process is essentially the reverse of what happens in your refrigerator, where heat is extracted from the inside to keep your food cold.
How is CO2 a Good Refrigerant?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is emerging as a strong contender in the world of refrigerants, and for good reason. Compared to traditional refrigerants, CO2 boasts several properties that make it an environmentally friendly and efficient choice. Let’s delve into the reasons why CO2 stands out.
Firstly, CO2 is a champion for environmental sustainability. Unlike many conventional refrigerants, CO2 has a zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) and an ultra-low Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 1. This means it doesn’t contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer or significantly enhance greenhouse gas effects. In a world increasingly focused on combating climate change, CO2 presents a much greener alternative. And unfortunately, the world has more CO2 than in the past centuries because of how much fossil fuels we have burned.
Beyond its environmental benefits, CO2 shines in terms of performance. It boasts excellent heat transfer properties. CO2 can absorb and release heat very effectively, leading to faster cooling and heating cycles in refrigeration systems. This translates to improved efficiency and lower energy consumption for your building. Additionally, CO2’s high density allows for smaller pipes and compressors to be used in refrigeration systems, making them more compact and potentially less expensive.

What are the Downsides of Using CO2 as Refrigerant in a Heat Pump System?
It’s important to acknowledge that CO2 does have some drawbacks. Due to its high operating pressures, CO2 systems require sturdier components compared to traditional refrigerants. This can translate to higher upfront costs for installation by welding steel vs brazing copper refrigerant lines. Additionally, CO2’s effectiveness can be reduced in very cold climates, as it can transition from a liquid to a gas state at higher temperatures than some other refrigerants.
However, some new companies like Tequs in Norway are combining the promise of hydronic systems (hot water) with CO2 Heat Pump systems. The CO2 refrigerant is contained within the outdoor heat pump system, and ultra hot or cold water is piped through the building to indoor fan coil units, or even into existing ductwork systems. This exciting system has a lot of potential, possibly lower costs for installation, and far lesser environmental impact over Freon. And, way less energy usage like all heat pump systems.
What About American CO2 Heat Pump Companies?
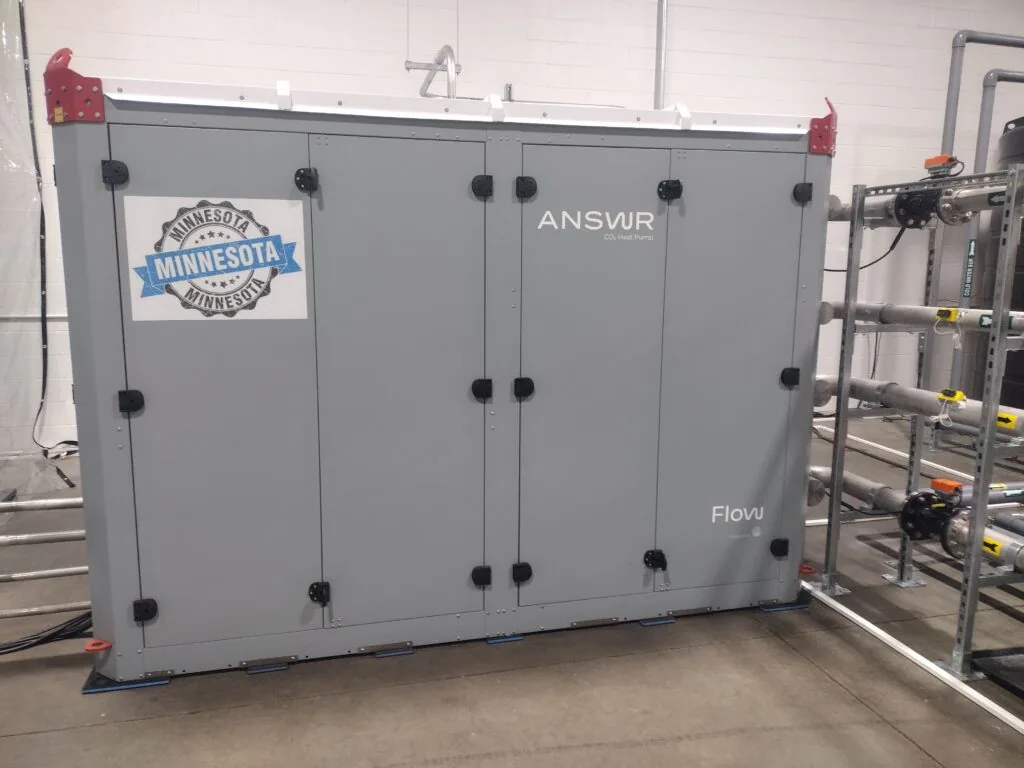
In fact, there are some exciting new American designed and manufactured CO2 heat pump systems. In July, Verde was able to tour the headquarters of Flow Environmental Systems in Minneapolis. Flow is a Minnesota-based engineering company specializing in environmentally friendly HVAC&R (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration) technologies. Their primary focus is on developing and manufacturing innovative heat pumps that utilize carbon dioxide as a refrigerant.
Based in Hennepin County, Minnesota, which has very low winter temperatures, this company is on the cutting edge of industrial heat pumps. They have patented heat pump technology that uses carbon dioxide as a refrigerant to be more efficient, operate in wider temperature ranges, and be more environmentally friendly.
With decades of industrial refrigeration, this team is putting together a product that will solve a lot of industry problems including on tool to replace steam heat, large scale refrigeration systems, and total building cooling. We saw one of their “ANSWR”s in action.
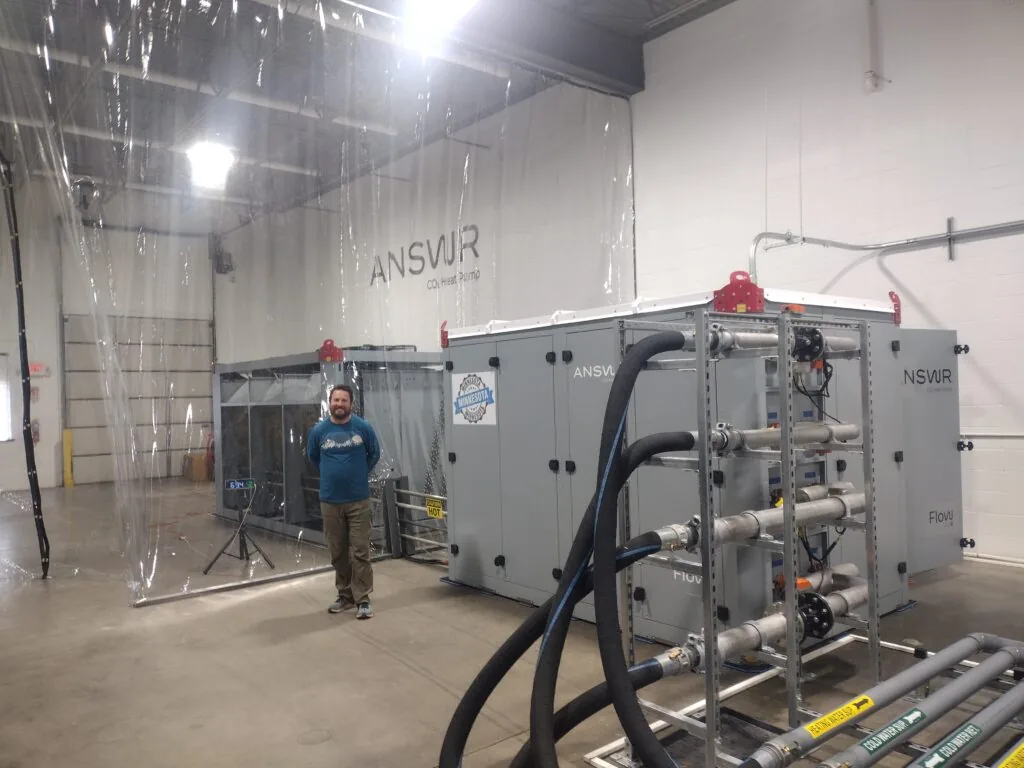

Built to be modularly serviced and repair after lots of experience in the industry – these impressive pieces of equipment can really drive large amounts of water to a very high temperature – solving problems in the HVACR industry that VRF air sourced heat pumps cannot currently accomplish.
They can also combine their systems into three designs, which is clever. All of these systems deliver water up to 180 degrees, which is incredibly advanced.
First, you can design a simple Water-to-Water Heat Pump, which are used for hydronic distribution systems. These heat pumps feature true simultaneous heating and cooling so that they can provide multiple duties with one power feed. Typical applications include Chillers, Boilers, DHW, Central Plants, and Heat Recovery. The capacity range is about 300 MBH to 2000 MBH.
Next, you can design Split Air to Water Heat Pumps. These systems can also be matched or unmatched load heat recovery devices. Split systems are helpful for applications where it is beneficial to locate the heat pump and gas cooler in separate locations for either space or mechanical or electrical restraints. Typically, a heat pump would be in a mechanical room, and the gas cooler would be outside. These heat pumps feature true simultaneous heating and cooling so that they can provide multiple duties with one power feed. These can get to a slightly lower 1400 MBH maximum on a single system. These systems involve more piping between the inside and outside areas, with higher installation costs.
Finally, you can have Packaged Air to Water Heat Pumps, which are used for hydronic distribution systems. These systems can also be matched or unmatched load heat recovery devices. Advanced defrost design. Packaged systems make installation very easy and are typically installed outside. Units come 100% assembled and tested. Just install the unit and hook up water and power; there is no need for refrigerant piping onsite. These heat pumps feature true simultaneous heating and cooling so that they can provide multiple duties with one power feed and include advanced defrost.
How Can You Use Hydronic (Hot Water) in a Heat Pump System?
Heat pumps are renowned for their efficient heating and cooling capabilities. But what if you crave the even distribution of heat and the silent operation offered by hydronic systems, traditionally reliant on boilers? The good news is, you can have the best of both worlds! Here’s how heat pumps can seamlessly integrate with hydronic systems.
The magic lies in air-to-water heat pumps. Unlike traditional air-source heat pumps that directly blow heated or cooled air throughout your home, air-to-water models extract heat from outdoor air and transfer it to a circulating water loop. This heated water then becomes the workhorse, silently flowing through your existing hydronic system’s network of pipes and radiators.
The benefits of this synergy are numerous. Firstly, heat pumps excel at extracting heat from even moderately cold outside air, making them efficient in most climates. This warm water then feeds your existing hydronic system, which is a master at evenly distributing heat throughout your home. Radiant floor heating, for example, provides a comfortable warmth that rises gently from the ground, eliminating drafts and hot and cold spots.
Furthermore, this marriage of technologies leverages the strengths of each system. Heat pumps are known for their efficiency, especially compared to traditional electric resistance heating. By using this efficient heat source to power your hydronic system, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption and enjoy lower running costs. Additionally, hydronic systems are inherently quiet, as they rely on the silent circulation of water. This, combined with the quiet operation of modern heat pumps, creates a remarkably peaceful heating and cooling experience.
What Problem Do CO2 Heat Pumps Solve?
Converting a boiler system to a heat pump system is often a complex and costly endeavor. One of the primary challenges lies in the fundamental differences between the two systems. Boilers generate heat through combustion, whereas heat pumps extract heat from the environment. This requires significant modifications to the heating system’s infrastructure. Existing piping and radiators may not be suitable for the lower temperatures produced by heat pumps, requiring potential upgrades or replacements. So currently, it is very expensive and intrusive on building occupants to install current heat pump technology.
Furthermore, heat pumps operate most efficiently in milder climates. In colder regions, their performance can decline, necessitating additional equipment like backup heating systems. While this backup heat only serves the coldest dozen days of the year, it is far less efficient than heat pump systems.
Another hurdle is the upfront cost. Replacing a boiler with a heat pump is generally more expensive initially. While the long-term energy savings can offset this cost over time, the upfront investment can be prohibitive for building owners. Additionally, the installation process can be disruptive, requiring significant labor and time. Fortunately, we expect a lot of federal, state and local utility incentives to help offset this cost.
Lastly, the complexity of the conversion process often requires specialized expertise. While many HVAC technicians are familiar with heat pumps, converting a boiler system to a heat pump system demands a deeper understanding of both technologies. Finding a qualified installer can be challenging, and the cost of their services can add to the overall project expense.
The Benefits of CO2 Heat Pumps
The potential benefits of improved efficiency, even heat distribution, and quiet operation make the combination of heat pumps and hydronic systems a compelling choice for many Illinois buildings. And since 60% of our buildings are going to need to transition away from natural gas by 2050 – we need every trick in our toolbelt to get there. Using Hot and Cold water lines combined with heat pumps is a great strategy to get there. And this technology is only at the beginning – with big improvements to come in the next few years to bring down costs, improve efficiency and see more of these in action in Illinois.
Overall, CO2 presents a compelling option for the future of refrigeration. Its environmental benefits, exceptional heat transfer properties, and potential for efficiency gains make it a strong contender. While some challenges exist, ongoing advancements in technology are continuously improving CO2 systems, making them a viable and sustainable solution for a variety of commercial and residential applications.
Reach out to Verde for an energy efficiency assessment today for your commercial building in Illinois. Whether you consider a high efficiency replacement or a Very High Efficiency system replacement, we are h ere to help and advise.
Featured Posts

Mar 15 2021
Energy Savings Formula
In 2002, I became a firefighter in the north suburbs of Chicago. I was young and idealistic - loving almost every part of the job. However, I had another secret passion - sustainability. In addition…
Continue Reading >

May 02 2019
Verde Energy Efficiency Experts 10 Most Sustainable Companies in Chicago
In our energy efficiency consulting firm, we constantly look for inspiration from local companies that lead and innovate in clean energy and sustainability. Not all companies have billion dollar budgets, but that doesn’t mean that…
Continue Reading >
Related Articles

Sep 23 2024
Utility Heat Pump Incentives for HVAC
Dual fuel heat pump packaged rooftop units (RTUs) offer a versatile and energy-efficient solution for heating and cooling commercial buildings. By combining the efficiency of a heat pump with the power of a gas furnace,…
Continue Reading >

Apr 26 2024
What is the Difference Between Air Source Heat Pumps and Geothermal?
Geothermal and air source heat pumps have a lot in common - in fact, they are essentially the same technology, just using a different way to expel and capture heat. One uses the air, and…